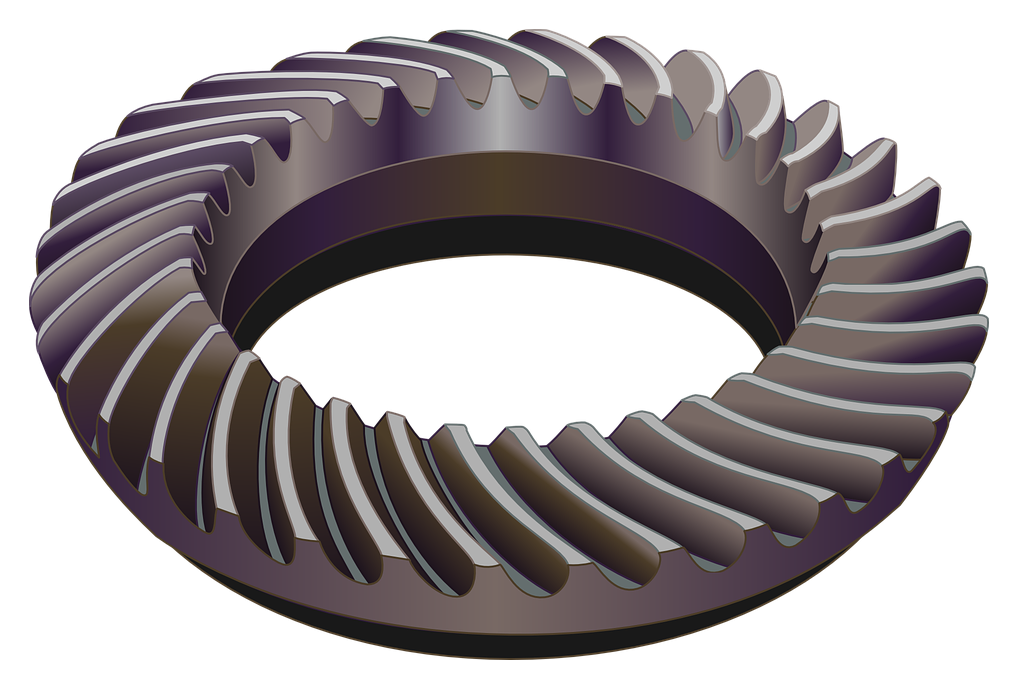
Product Description
Product introduction
| Gear model | Customized gear shaft accoding to customers sample or drawing |
| Processing machine | CNC machine |
| Material | 20CrMnTi/ 20CrMnMo/ 42CrMo/ 45#steel/ 40Cr/ 20CrNi2MoA |
| Heat treattment | 20CrMnTi/ 20CrMnMo/ 42CrMo/ 45#steel/ 40Cr/ 20CrNi2MoA |
| Hardness | 58-62HRC |
| Qaulity standerd | GB/ DIN/ JIS/ AGMA |
| Accuracy class | 5-8 class |
| Shipping | Sea shipping/ Air shipping/ Express |
Factory introduction
HangZhou HangZhoung Engine Parts Co., LTD is set product development, production and sales of specialized enterprises, the company was founded in 1985, is located in Xihu (West Lake) Dis. Bridge River, 50 kilometers from the provincial capital HangZhou city, convenient transportation.
The company has modern professional production workshop covers an area of 30,000 square meters, 120 employees, including professional and technical staff of 30 people. In the past 30 years, the company to adapt to the increasing market demand of advanced production equipment to develop new products. Research and development to produce piston and engine bearing with many kinds materials. In 2007, commissioned the development of a new project: the production and processing gear, the introduction of Germany, Japan advanced processing center equipment to meet agricultural machinery, automobiles, construction machinery, and other aspects of the production. The company has been appraised as ZheJiang quality products, corporate credit quality units. The company has offices in HangZhou.
Our products sell well in China and exported to Europe, the Americas, the Middle East, Southeast Asia and other countries. My company adhered to the "good faith, winning by quality, first-class service will be presented to our customers" for the purpose, we are willing to be honest with you, and work together for a better tomorrow.
Factory pictures and cerfitication
/* January 22, 2571 19:08:37 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(",").forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Agricultural Machinery |
|---|---|
| Hardness: | Hardened Tooth Surface |
| Gear Position: | External Gear |
| Manufacturing Method: | Rolling Gear |
| Toothed Portion Shape: | Bevel Wheel |
| Material: | 20crmnti |
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
How do spiral gears handle variations in tooth engagement during operation?
Spiral gears are designed to handle variations in tooth engagement during operation effectively. The unique helical tooth arrangement of spiral gears allows them to accommodate these variations and provide several benefits. Here's how spiral gears handle variations in tooth engagement:
- Gradual Engagement: One of the key advantages of spiral gears is their ability to achieve gradual tooth engagement. As the gears rotate, the helical shape of the teeth allows them to come into contact gradually, starting from one end of the gear to the other. This gradual engagement minimizes the impact and shock that would occur with sudden full tooth contact in other gear types. It results in smoother and quieter operation, reducing noise, vibrations, and stress on the gear system.
- Increased Tooth Contact Area: Spiral gears provide a larger tooth contact area compared to straight-cut or spur gears. The helical tooth profile extends the contact length along the gear face, distributing the load over multiple teeth at any given moment. This increased contact area enables spiral gears to handle higher loads and transmit torque more efficiently.
- Load Sharing: Due to the helical arrangement, spiral gears naturally distribute the load across multiple teeth. This load-sharing characteristic helps to minimize tooth wear and fatigue. As the gears rotate, different teeth come into contact, ensuring that the load is distributed evenly. This load sharing capability enhances the gear system's durability and extends its service life, particularly in applications with fluctuating loads.
- Reduction of Side Thrust: Spiral gears generate an axial thrust force during operation. However, by using pairs of spiral gears with opposite helix angles, this side thrust force can be greatly reduced or even eliminated. When paired gears with opposite helix angles mesh together, the axial thrust forces cancel each other out. This eliminates the need for additional thrust bearings or complex gear arrangements to counteract the axial forces, simplifying the gear system design.
- Improved Lubrication: The helical tooth profile of spiral gears promotes better lubrication. The continuous sliding motion between the teeth creates a pumping action that helps distribute lubricant along the tooth surfaces. This improved lubrication reduces friction, heat generation, and wear, enhancing the overall efficiency and longevity of the gear system.
These features of spiral gears—gradual engagement, increased tooth contact area, load sharing, reduction of side thrust, and improved lubrication—make them highly effective in handling variations in tooth engagement during operation. Spiral gears are commonly used in various applications such as automotive transmissions, industrial machinery, and power generation systems, where smooth and reliable power transmission is crucial.
How do you calculate the gear ratio in a spiral gear system?
The gear ratio in a spiral gear system can be calculated by comparing the number of teeth on the driving gear (pinion) to the number of teeth on the driven gear (gear). The gear ratio represents the ratio of the angular velocity (speed) of the driving gear to the angular velocity of the driven gear. Here's the formula to calculate the gear ratio:
Gear Ratio = Number of Teeth on Driven Gear / Number of Teeth on Driving Gear
For example, consider a spiral gear system where the driving gear (pinion) has 20 teeth, and the driven gear (gear) has 40 teeth. The gear ratio can be calculated as follows:
Gear Ratio = 40 / 20 = 2
In this example, the gear ratio is 2, which means the driven gear will rotate at half the speed of the driving gear. This calculation assumes that the gears have the same module (gear size) and that there are no additional gear stages in the system.
It's important to note that the gear ratio determines the speed and torque relationship between the driving and driven gears. A gear ratio greater than 1 (e.g., 2, 3, etc.) indicates a reduction in speed and an increase in torque, while a gear ratio less than 1 (e.g., 0.5, 0.75, etc.) indicates an increase in speed and a reduction in torque.
When working with spiral gears, it's essential to consider the helix angle and axial thrust in addition to the gear ratio to ensure proper gear design and performance.
How do spiral gears contribute to smoother and quieter gear engagement?
Spiral gears, also known as helical gears, offer several design features that contribute to smoother and quieter gear engagement compared to other gear types. Here's how spiral gears achieve this:
- Gradual Tooth Engagement: The helical tooth arrangement in spiral gears allows for gradual tooth engagement as the gears mesh. Unlike straight-cut gears, where the teeth make sudden contact, spiral gears have angled teeth that come into contact gradually. This gradual engagement helps to reduce impact and noise during gear meshing.
- Increased Contact Ratio: The helical tooth design of spiral gears provides a higher contact ratio compared to straight-cut gears. The contact ratio refers to the number of teeth in mesh at any given time. With a higher contact ratio, the load is distributed over multiple teeth, resulting in reduced stress on individual teeth and smoother gear operation.
- Reduced Sliding Friction: The helical tooth arrangement in spiral gears helps minimize sliding friction between the teeth. As the teeth mesh, the angled surfaces slide against each other instead of making direct contact. This sliding action reduces friction and wear, leading to smoother operation and reduced noise levels.
- Efficient Load Distribution: Spiral gears distribute the load over multiple teeth due to their helical tooth arrangement. This distribution of load helps to evenly distribute the forces and minimize localized stresses. By spreading the load, spiral gears can handle higher torque transmission and carry heavier loads, resulting in smoother and more reliable gear engagement.
- Axial Thrust Compensation: Spiral gears can be designed with opposite helix angles on mating gears. This configuration helps cancel out the axial thrust generated during gear meshing. By eliminating or reducing the axial thrust, spiral gears reduce the need for additional thrust bearings and simplify the gear design, contributing to smoother operation.
These design features of spiral gears, including gradual tooth engagement, increased contact ratio, reduced sliding friction, efficient load distribution, and axial thrust compensation, work together to provide smoother and quieter gear engagement. These characteristics make spiral gears ideal for applications where noise reduction, smooth operation, and reliable gear meshing are essential.
editor by Dream 2024-04-23